pelvic2
AIDAs tredje ansökningsomgång avslutad
Tre nya projekt antogs i den sista ansökningsomgången från AIDA under 2017. Arbetet för de sammanlagt nio projekten är i full gång och varje månad arrangeras AIDA-dagar på CMIV där deltagarna får möjlighet att nätverka och utnyttja infrastrukturen. Det ingår även möten och föreläsningar under dessa dagar för att hjälpa till i projektens utveckling.
Interactive deeplearning segmentation for decision support in neuroradiology
Robin Strand, Uppsala University
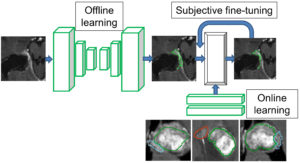
Many brain diseases can damage brain cells (nerve cells), which can lead to loss of nerve cells and, secondarily, loss of brain volume. Even slight loss of nerve cells can give severe neurological and cognitive symptoms. Technical imaging advancements allow detection and quantification of very small tissue volumes in magnetic resonance (MR) neuroimaging. Due to the enormous amount of information in a typical MR brain volume scan, and difficulties such as partial volume effects, noise, artefacts, etc., interactive tools for computer aided analysis are absolutely essential for this task.
In this project, we will develop and evaluate interactive deep learning segmentation methods for quantification and treatment response analysis in neuroimaging. Interaction speed will be obtained by dividing the segmentation procedure into an offline pre-segmentation step and an on-line interactive loop in which the user adds constraints until satisfactory result is obtained. See the conceptual illustration.
The successful outcome of this project will allow detailed correct diagnosis, as well as accurate and precise analysis of treatment response in neuroimaging, in particular in quantification of intracranial aneurysm remnants and brain tumors (Gliomas WHO grades III and IV) growth.
Automatic detection of lung emboli in CTPA examinations
Tobias Sjöblom, Uppsala University
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a serious condition in which blood clots travel to, and occlude, the pulmonary arteries. To diagnose or exclude PE, radiologists perform CT pulmonary angiographies (CTPA). Each CTPA consists of hundreds of images. Manual CTPA interpretation is, therefore, not only time-consuming, but is also dependent on human factors, especially in the stressful conditions of emergency medical care. Several automatic PE detection systems have been developed, but none with acceptable accuracy for clinical usage.
Our team will combine expertise in clinical radiology, medical image processing and analysis, and diagnostic technologies to develop a system for fast, precise and reliable automatic identification of pulmonary embolization in CTPA examinations. The availability of a large set of annotated CTPA examinations, which is assembled by our team, is a particular asset which enables development and training of advanced deep learning methods to address the task. We therefore expect to reach performance required for usage in a daily clinical practice.
The resulting system will save precious time of both patients suspected of having PE and of expert radiologists during their daily clinical routines. This will, in turn, have a strong positive impact on the health system in Sweden, considering that CTPA is today one of the most common emergency CT examinations in the country.
Simultaneous landmark detection and organ segmentation in medical images for orthopedic surgery planning
Chunliang Wang, KTH, Stockholm
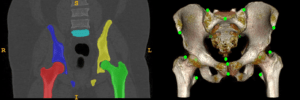
Landmark detection and organ segmentation are common tasks in medical image analysis. In this project, we aim to develop a multi-task deep neural network that can simultaneously detect multiple landmarks and segment several key structures. These multi-task networks can often deliver better results than the single-task models. The proposed algorithm will be tested in a hip surgery planning system using 3D CT images, where the segmentation results will provide graphical representation of the bones and the detected landmarks can be used to extract key measurements for the planning procedure. This will simplify and speedup the orthopedic surgery planning by replacing the most time-consuming step of landmark marking and joint attribute measurements in 3D CT images with automated tools. By simplifying the operation of the planning software, we hope to reduce risk-taking in clinical practice due to the cumbersome planning procedure and improve the outcome of the surgery.
AKTUELLT
Glad sommar önskar vi från Medtech4Health
Efter en intensiv vår är det snart dags för en välbehövlig sommarpaus. Men först ser vi fram emot att ses i Almedalen där vi är en del av mötesplatsen Tillsammans.
SO Västra stärker innovationskraften genom samverkan och erfarenhetsutbyte
Medtech4Healths nod SO Västra har gjort programmet till en naturlig del av innovationsarbetet i Västra Götaland. Här finns en stark samverkan där metoder och erfarenheter delas framgångsrikt.
Nytt verktyg ska bana vägen för smidigare breddinförande av medicinteknik
Först ut från Medtech4Healths strategiska projekt MedImpact är ett instrument för enklare breddinförande av teknik för egenmonitorering. Med instrumentets frågebatteri blir det möjligt att undvika fallgroparna vid ett breddinförande. Instrumentet finns på Medtech Arena.
Nya satsningar ska göra det lättare för små innovativa medicintekniska företag
Regeringen har gett flera nya uppdrag till myndigheter som arbetar med medicinteknik. Målet är att stärka sjukvården och förbättra Sveriges beredskap vid kriser.
NYHETSBREV
Följ nyheter och utlysningar från Medtech4Health - prenumera på vårt nyhetsbrev.